Tests on bitumen
There are a number of tests to assess the properties of bituminous materials. The following tests are usually conducted to evaluate different properties of bituminous materials.- Penetration test
- Ductility test
- Softening point test
- Specific gravity test
- Viscosity test
- Flash and Fire point test
- Float test
- Water content test
- Loss on heating test
Penetration test
It measures the hardness or softness of bitumen by measuring the depth in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard loaded needle will penetrate vertically in 5 seconds. BIS had standardized the equipment and test procedure. The penetrometer consists of a needle assembly with a total weight of 100g and a device for releasing and locking in any position. The bitumen is softened to a pouring consistency, stirred thoroughly and poured into containers at a depth at least 15 mm in excess of the expected penetration. The test should be conducted at a specified temperature of 25 C. It may be noted that penetration value is largely influenced by any inaccuracy with regards to pouring temperature, size of the needle, weight placed on the needle and the test temperature. A grade of 40/50 bitumen means the penetration value is in the range 40 to 50 at standard test conditions. In hot climates, a lower penetration grade is preferred. The Figure below shows a schematic Penetration Test setup.
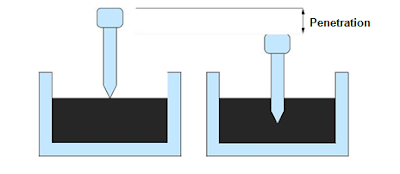 |
| Penetration Test Setup |
Ductility test
Ductility is the property of bitumen that permits it to undergo great deformation or elongation. Ductility is de ned as the distance in cm, to which a standard sample or briquette of the material will be elongated without breaking. The dimension of the briquette thus formed is exactly 1 cm square. The bitumen sample is heated and poured in the mould assembly placed on a plate. These samples with moulds are cooled in the air and then in water bath at 27 C temperature. The excess bitumen is cut and the surface is leveled using a hot knife. Then the mould with assembly containing sample is kept in water bath of the ductility machine for about 90 minutes. The sides of the moulds are removed, the clips are hooked on the machine and the machine is operated. The distance up to the point of breaking of thread is the ductility value which is reported in cm. The ductility value gets affected by factors such as pouring temperature, test temperature, rate of pulling etc. A minimum ductility value of 75 cm has been specified by the BIS. Figure below shows ductility moulds to be filled with bitumen.
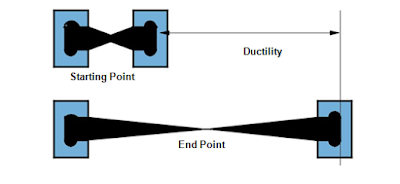 |
| Ductility Test |
Softening point test
Softening point denotes the temperature at which the bitumen attains a particular degree of softening under the specifications of the test. The test is conducted by using Ring and Ball apparatus. A brass ring containing test sample of bitumen is suspended in liquid like water or glycerin at a given temperature. A steel ball is placed upon the bitumen sample and the liquid medium is heated at a rate of 5 C per minute. Temperature is noted when the softened bitumen touches the metal plate which is at a specified distance below. Generally, higher softening point indicates lower temperature susceptibility and is preferred in hot climates. Figure below shows Softening Point test setup.
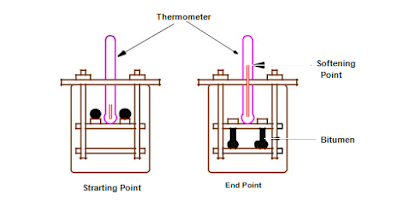 |
| Softening Point Test |
Specific gravity test
In paving jobs, to classify a binder, density property is of great use. In most cases, bitumen is weighed, but when used with aggregates, the bitumen is converted to volume using density values. The density of bitumen is greatly influenced by its chemical composition. Increase in aromatic type mineral impurities causes an increase in specific gravity.
The specific gravity of bitumen is defined as the ratio of mass of given volume of bitumen of known content to the mass of equal volume of water at 27 C. The specific gravity can be measured using either pycnometer or preparing a cube specimen of bitumen in semi-solid or solid state. The specific gravity of bitumen varies from 0.97 to 1.02.
Viscosity test
Viscosity denotes the fluid property of bituminous material and it is a measure of resistance to low. At the application temperature, this characteristic greatly influences the strength of resulting paving mixes. Low or high viscosity during compaction or mixing has been observed to result in lower stability values. At high viscosity, it resists the compacitive e ort and thereby resulting mix is heterogeneous, hence low stability values. And at low viscosity instead of providing a uniform film over aggregates, it will lubricate the aggregate particles. Orifice type viscometers are used to indirectly nd the viscosity of liquid binders like cutbacks and emulsions. The viscosity expressed in seconds is the time taken by the 50 ml bitumen material to pass through the orifice of a cup, under standard test conditions and specified temperature. The viscosity of a cutback can be measured with either 4.0 mm orifice at 25 C or 10 mm orifice at 25 or 40 C.
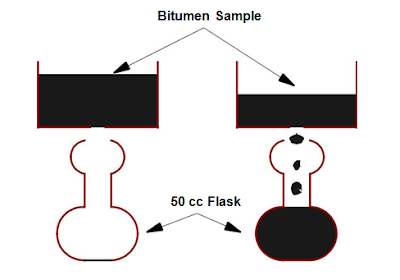 |
| Viscosity Test |
Flash and fire point test
At high temperatures depending upon the grades of bitumen, materials leave out volatiles. And these volatiles catches fire which is very hazardous and therefore it is essential to qualify this temperature for each bitumen grade. BIS de ned the ash point as the temperature at which the vapour of bitumen momentarily catches fire in the form of ash under speci ed test conditions. The are point is de ned as the lowest temperature under speci ed test conditions at which the bituminous material gets ignited and burns.
Float test
Normally the consistency of bituminous material can be measured either by penetration test or viscosity test. But for certain range of consistencies, these tests are not applicable and Float test is used. The apparatus consists of an aluminum float and a brass collar filled with bitumen to be tested. The specimen in the mould is cooled to a temperature of 5 C and screwed in to float. The total test assembly is oated in the water bath at 50 C and the time required for water to pass its way through the specimen plug is noted in seconds and is expressed as the float value.
Water content test
It is desirable that the bitumen contains minimum water content to prevent foaming of the bitumen when it is heated above the boiling point of water. The water in a bitumen is determined by mixing known weight of specimen in a pure petroleum distillate free from water, heating, and distilling off the water. The weight of the water condensed and collected is expressed as percentage by weight of the original sample. The allowable maximum water content should not be more than 0.2% by weight.
Loss on heating test
When the bitumen is heated it loses the volatility and gets hardened. About 50 gm of the sample is weighed and heated to a temperature of 163 C for 5 hours in a specified oven designed for this test. The sample specimen is weighed again after the heating period and loss in weight is expressed as percentage by weight of the original sample. Bitumen used in pavement mixes should not indicate more than 1% loss in weight, but for bitumen having penetration values 150-200 up to 2% loss in weight is allowed.
![[PDF] SP 16 :1980 Design Aids For Reinforced Concrete to IS : 456-1978](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3vWyWR9sVpY2Mcip5F3ttq_4jje6Et0mqiBug-q8n7kClvXle3KD0XtZBwYBtmYFfIekvQYIW9gFB5aqcri6KrHD4x2PalOyEWAXPkLNFfbXe8m9m8WvCLSEWok7vPivvYidB1tj8JjeX/w100/is-sp-16-1980.JPG)

![Different Applications of GIS [ Geographical Information System ]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhHuGl0hPEHKOfNPmTyBacOw3n4QQS54eRbfvEJfHxbOdImzfdroP0ab3tvCp98S2P8ZvJWqiz1clCwaQGVp2i9t9Nq4UkvRgcIR9X_chyphenhyphenkBJmhr4UIJRs4Jw0ppSn6jn56sVfBed4j9i7J/w100/8113229957_421c837a06_b.jpg)



![[PDF] Download IS 800 Code | Indian Standard Code for Steel](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjMmVdQd3q6sKYLbOG23DVJg2U_8IrdWJSfCcyA7gKs5NKVFBsi6dFPhGxoVctqzOHEIvJ6pqvQ6mpFMd5vV0U5IQHo-FETwRXTjbZ-Dok9CHxUJgePxHyFTHa2pNiWyW4mkYCJWOv_2IcP/w100/is-800-2007.JPG)
![[PDF] IS 456 2000 | Download Civil Engineering Code](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjl8mzhZI_smGwhJPipCx2TuxHldgAvnHrYfkud8mDJ1kF4Syd83-TNKsXjyY1BVxFrxZ1tt-fErpupgiF146wqOfPtGo8M9GWrnQX9b9TyA-YtjlNWnlwdk9LaMN_JJN8AGCU619UI6Uu_/w100/is-456-2000.JPG)
0 Comments