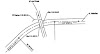
Right of Way:
Right of way is the area of land acquired and reserved for construct and development of road along its alignment. The width of this acquired land is called land width and it depends upon the width of formation, slope of cuttings and embankments, minimum sight distance on horizontal curves, drainage system and also on the importance of the road and possible future development.
Formation Width:
Is the sum of widths of carriage way or pavements, shoulders and separators if any. It is the top width of the highway cutting exclusive the side drains.
Frontage Roads:
These are provided to give access properties along an important highway. The frontage road may be run parallel to the highway & the isolated by separators.
Road Margins:
Road margins are the portions of the land on either side of the road way of a road. The various elements included in the road margins are parking lane, frontage road, drive way, cycle track, footpath, guard rails and embankment slope.
Width of pavement or carriage way:
Carriage way is the width of roadway constructed for movement of vehicular traffic carriage way width depends in the width of traffic lane and no of lane required. The numbers of lane required on a highway depends upon predicted and traffic capacity of each lane. The lane width required is calculated in the basic of the width of vehicle and minimum side clearance required for safe drive.
Parking lane:
These are provided in urban roads to allow parking. Parallel parking should be allowed as far as possible. The width of parking lane should be sufficient.
Drive Way:
These connect the highway with commercial establishment like fuel stations service station etc.
Cycle Track:
These are provided in urban areas where the volume of cycle traffic on the road is very high. The min width of 2 m is provided for the cycle track & it may be increased by 1m for each additional track.
Footpath:
In urban area where the vehicular as well as pedestrian traffic are heavy footpaths are provided to avoid accidents.
Guard Rails:
These are provided at the edge of shoulder when the road is constructed on a fill of height more than 3 m to prevent the vehicle from running of the track.
Shoulder:
These are the portion of the road way between the outer edges of carriage way & edges of top surface of embankment or inner edges of the side drains in cutting. These are provided along the road edge to use in an emergency lane for vehicle required to be taken out of the pavement or road way. Min width of shoulder 4.6 m is desirable so that a vehicle station at the side of the shoulder would have a clearance of about 1.85 m from the pavement edge.
Side Slopes or Camber:
These are the slopes provided of the side of earth work of the road in embankment in cutting for its stability; side slopes in the road are so design as to keep the earthwork stable in embankment or in cutting. The nature of soil in earth work, climate conditions, method of drainage provided etc or the factors which affect the design of side slope.
Kerbs:
Kerbs are the boundaries between the pavement & shoulders or footpath.





![[PDF] Download IS 800 Code | Indian Standard Code for Steel](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjMmVdQd3q6sKYLbOG23DVJg2U_8IrdWJSfCcyA7gKs5NKVFBsi6dFPhGxoVctqzOHEIvJ6pqvQ6mpFMd5vV0U5IQHo-FETwRXTjbZ-Dok9CHxUJgePxHyFTHa2pNiWyW4mkYCJWOv_2IcP/w100/is-800-2007.JPG)
![[PDF] IS 456 2000 | Download Civil Engineering Code](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjl8mzhZI_smGwhJPipCx2TuxHldgAvnHrYfkud8mDJ1kF4Syd83-TNKsXjyY1BVxFrxZ1tt-fErpupgiF146wqOfPtGo8M9GWrnQX9b9TyA-YtjlNWnlwdk9LaMN_JJN8AGCU619UI6Uu_/w100/is-456-2000.JPG)

![[PDF] SP 16 :1980 Design Aids For Reinforced Concrete to IS : 456-1978](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3vWyWR9sVpY2Mcip5F3ttq_4jje6Et0mqiBug-q8n7kClvXle3KD0XtZBwYBtmYFfIekvQYIW9gFB5aqcri6KrHD4x2PalOyEWAXPkLNFfbXe8m9m8WvCLSEWok7vPivvYidB1tj8JjeX/w100/is-sp-16-1980.JPG)
0 Comments