Road classification
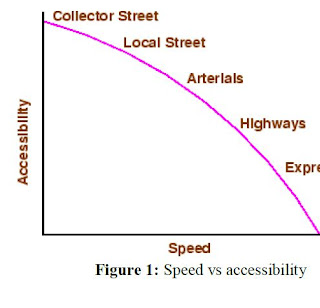
The roads can be classified in many ways. The classification based on speed and accessibility is the most generic one. Note that as the accessibility of road increases, the speed reduces. . Accordingly, the roads can be classified as follows in the order of increased accessibility and reduced speeds.Freeways:
Freeways are access-controlled divided highways. Most freeways are four lanes, two lanes each direction, but many freeways widen to incorporate more lanes as they enter urban areas. Access is controlled through the use of interchanges, and the type of interchange depends upon the kind of intersecting road way (rural roads, another freeway etc.)
Expressways:
They are superior type of highways and are designed for high speeds ( 120 km/hr is common), high traffic volume and safety. They are generally provided with grade separations at intersections. Parking, loading and unloading of goods and pedestrian traffic is not allowed on expressways.
Highways:
They represent the superior type of roads in the country. Highways are of two types - rural highways and urban highways. Rural highways are those passing through rural areas (villages) and urban highways are those passing through large cities and towns, ie. urban areas.
Arterials:
It is a general term denoting a street primarily meant for through traffic usually on a continuous route. They are generally divided highways with fully or partially controlled access. Parking, loading and unloading activities are usually restricted and regulated. Pedestrians are allowed to cross only at intersections/designated pedestrian crossings.
Local streets :
A local street is the one which is primarily intended for access to residence, business or abutting property. It does not normally carry large volume of traffic and also it allows unrestricted parking and pedestrian movements.
Collector streets:
These are streets intended for collecting and distributing traffic to and from local streets and also for providing access to arterial streets. Normally full access is provided on these streets . There are few parking restrictions except during peak hours.
National Highways
- They are main highways running through the length and breadth of India connecting major ports , foreign highways, capitals of large states and large industrial and tourist centers including roads required for strategic movements.
- It was recommended by Jayakar committee that the National highways should be the frame on which the entire road communication should be based.
- All the national highways are assigned the respective numbers.
- For e.g. the highway connecting Delhi-Ambala-Amritsar is denoted as NH-1 (Delhi-Amritsar), where as a bifurcation of this highway beyond Fullundar to Srinagar and Uri is denoted as NH-.
- They are constructed and maintained by CPWD.
- The total length of National highway in the country is 58,112 Kms, and constitute about 2% of total road networks of India and carry 40% of total traffic.
1. State highways
- They are the arterial roads of a state, connecting up with the national highways of adjacent states, district head quarters and important cities within the state
- They also serve as main arteries to and from district roads.
- Total length of all SH in the country is 1,37,119 Kms.
2. Major district roads
- Important roads with in a district serving areas of production and markets , connecting those with each other or with the major highways.
- India has a total of 4,70,000 kms of MDR.
3. Other district roads
- Roads serving rural areas of production and providing them with outlet to market centers or other important roads like MDR or SH.
4. Village roads
- They are roads connecting villages or group of villages with each other or to the nearest road of a higher category like ODR or MDR.
- India has 26,50,000 kms of ODR+VR out of the total 33,15,231 kms of all type of roads.

![[PDF] Download IS 800 Code | Indian Standard Code for Steel](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjMmVdQd3q6sKYLbOG23DVJg2U_8IrdWJSfCcyA7gKs5NKVFBsi6dFPhGxoVctqzOHEIvJ6pqvQ6mpFMd5vV0U5IQHo-FETwRXTjbZ-Dok9CHxUJgePxHyFTHa2pNiWyW4mkYCJWOv_2IcP/w100/is-800-2007.JPG)




![[PDF] SP 16 :1980 Design Aids For Reinforced Concrete to IS : 456-1978](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj3vWyWR9sVpY2Mcip5F3ttq_4jje6Et0mqiBug-q8n7kClvXle3KD0XtZBwYBtmYFfIekvQYIW9gFB5aqcri6KrHD4x2PalOyEWAXPkLNFfbXe8m9m8WvCLSEWok7vPivvYidB1tj8JjeX/w100/is-sp-16-1980.JPG)
![[PDF] IS 456 2000 | Download Civil Engineering Code](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjl8mzhZI_smGwhJPipCx2TuxHldgAvnHrYfkud8mDJ1kF4Syd83-TNKsXjyY1BVxFrxZ1tt-fErpupgiF146wqOfPtGo8M9GWrnQX9b9TyA-YtjlNWnlwdk9LaMN_JJN8AGCU619UI6Uu_/w100/is-456-2000.JPG)
